The Future of Intelligence: How Multi-Agent Systems Could Pave the Way to Ultra high intelligence
Jan 14, 2025
10 min Read
The concept of artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. But as AI continues to advance, a new frontier is emerging: Ultra-High Intelligence (UHI). Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on a singular entity performing tasks, UHI is driven by decentralized networks of agents - autonomous entities that collaborate, share knowledge, and solve complex problems together.
This shift to multi-agent systems marks a transformative step toward AI that is far more adaptable, scalable, and capable of tackling dynamic challenges.
In this blog, we’ll explore how multi-agent systems work and their potential to lay the groundwork for Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), a form of intelligence that could far surpass human capacity.
We’ll dive into how these systems operate, leveraging swarm intelligence, decentralized coordination, and incentivized collaboration, to address real-world problems in areas like supply chain management, healthcare, and finance. As we move toward a future where AI is collaborative rather than isolated, the possibilities are vast and the challenges just as significant. Join us as we explore how multi-agent systems might revolutionize AI, creating smarter, more resilient, and more scalable technologies for the future.
From Single-Agent to Multi-Agent Systems
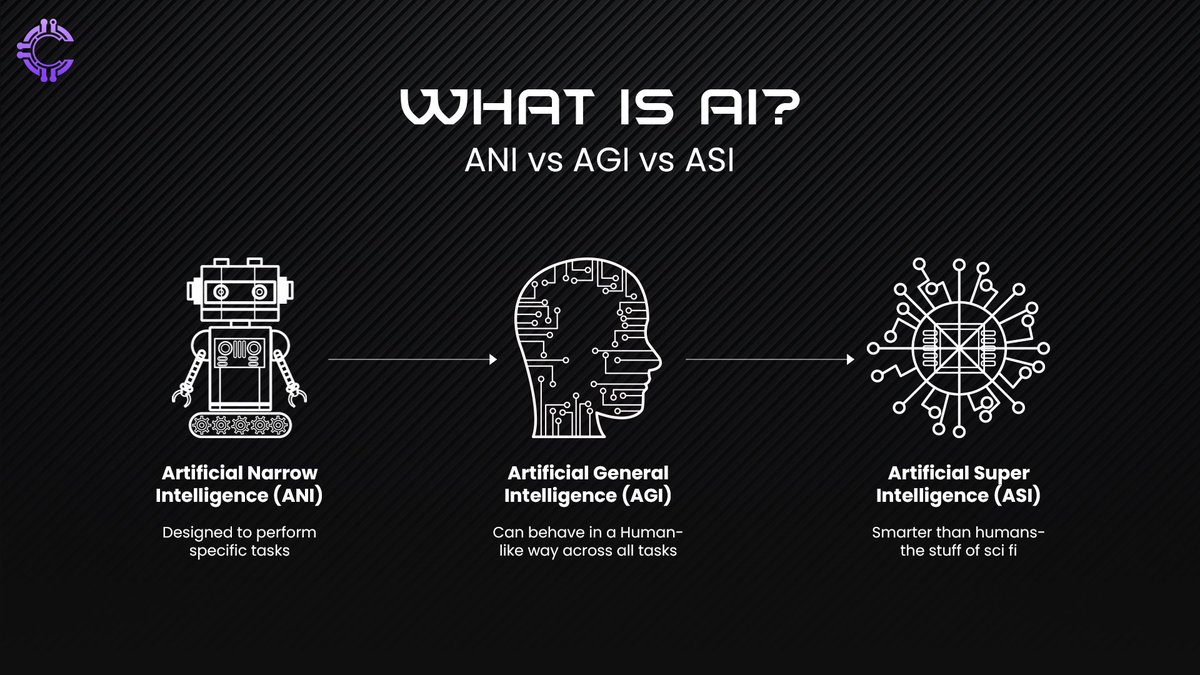
AI began its journey solving specific problems playing chess, recognizing faces, and optimizing logistics. These systems, classified as Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), excelled within defined boundaries but lacked the capacity to generalize or adapt.
The next ambitious target became Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), an ambitious pursuit of human-like intelligence capable of reasoning and learning across diverse domains. However, achieving AGI has proven elusive, raising the question: is human-like intelligence the ultimate goal?
A new contender has emerged Ultra-High Intelligence (UHI). Unlike AGI, UHI doesn’t strive to replicate human intelligence. Instead, it focuses on creating a system where intelligence is decentralized, emergent, and far beyond human capabilities. UHI leverages multi-agent systems to coordinate, adapt, and solve problems collaboratively, reshaping what intelligence can achieve.
What Are Multi-Agent Systems?
Multi-agent systems are networks of autonomous entities—agents—that interact, collaborate, and learn. These agents operate within a shared environment and communicate using defined protocols. Let’s break down their core components:
Agents: Independent entities capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and taking actions. Some agents are simple rule-followers, while others are equipped with machine learning capabilities.
Environment: The dynamic context in which agents operate. This could range from a digital network to a real-world supply chain. The complexity of the environment impacts the system’s adaptability and efficiency.
Communication: Agents exchange information through message-passing protocols or shared memory systems, enabling collaboration and synchronization.
Collaboration: Agents work together to achieve collective goals, sharing tasks, resolving conflicts, and leveraging collective intelligence.
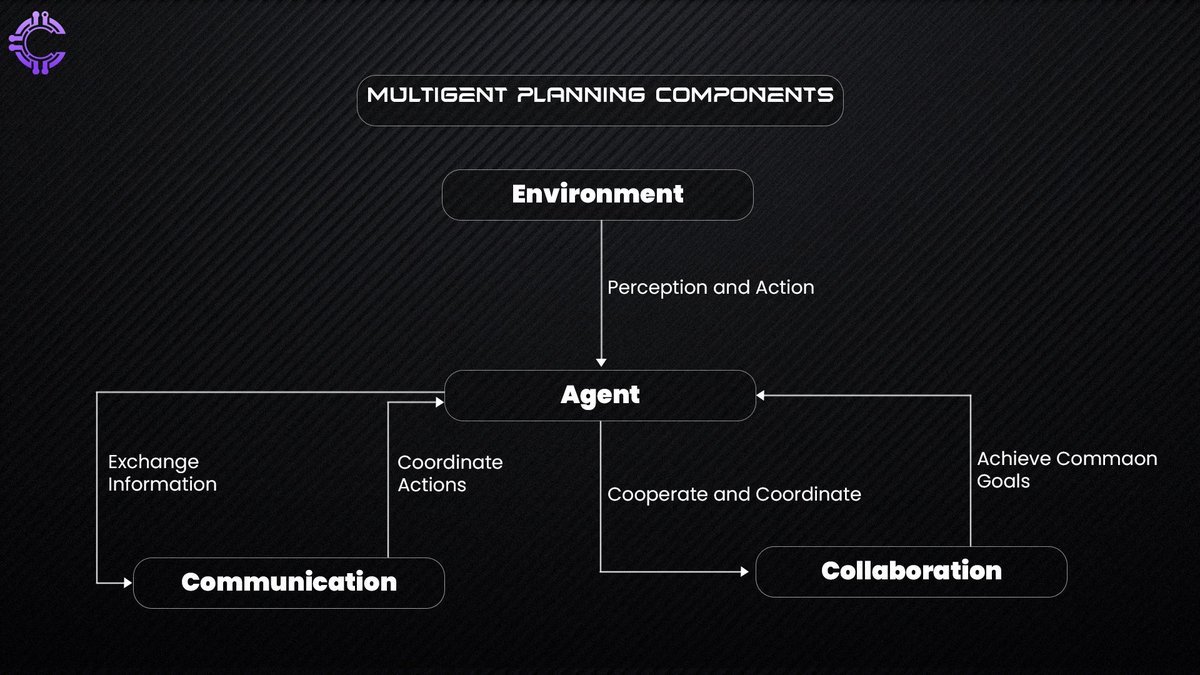
How does these decentralized multi-Agents engage?
In decentralized AI systems, collaboration isn’t just a luxury - it’s a necessity.
Coordination Without Central Authority
Unlike traditional centralized systems, decentralized AI agents operate on blockchain-based protocols. Through smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded directly on the blockchain - agents collaborate seamlessly without intermediaries. These contracts automate coordination, ensuring tasks are executed fairly and transparently.
For example, in supply chain management, multiple AI agents can autonomously track shipments, optimize routes, and ensure timely deliveries without human oversight. These agents collectively solve problems, relying on verifiable blockchain mechanisms to ensure trust and accountability.
Incentivized Collaboration Through Crypto-Economics
Collaboration in decentralized systems is fueled by tokenized incentives. Tokens reward agents for completing tasks or sharing knowledge, aligning their goals to foster cooperation. This system creates a win-win environment where collaboration becomes a necessity rather than an option.
In federated learning systems, agents train AI models collectively while maintaining data privacy. Blockchain ensures every agent’s contribution is recognized and rewarded, creating a self-sustaining ecosystem where AI systems improve without centralized control.
Dynamic Markets for Resource Sharing
Decentralized AI agents thrive in blockchain-powered marketplaces where computational resources, bandwidth, and data are traded. These tokenized resource markets create dynamic environments where agents bid for what they need. This setup not only optimizes efficiency but also drives competition, fostering innovation.
Trust Through Technology
In decentralized ecosystems, trust is embedded in code. Advanced cryptographic methods like zero-knowledge proofs ensure secure, tamper-proof communication. Decentralized identity systems safeguard agent authenticity, preventing malicious activities like identity spoofing or Sybil attacks.
Multi-Agent Systems vs. Traditional AI agent
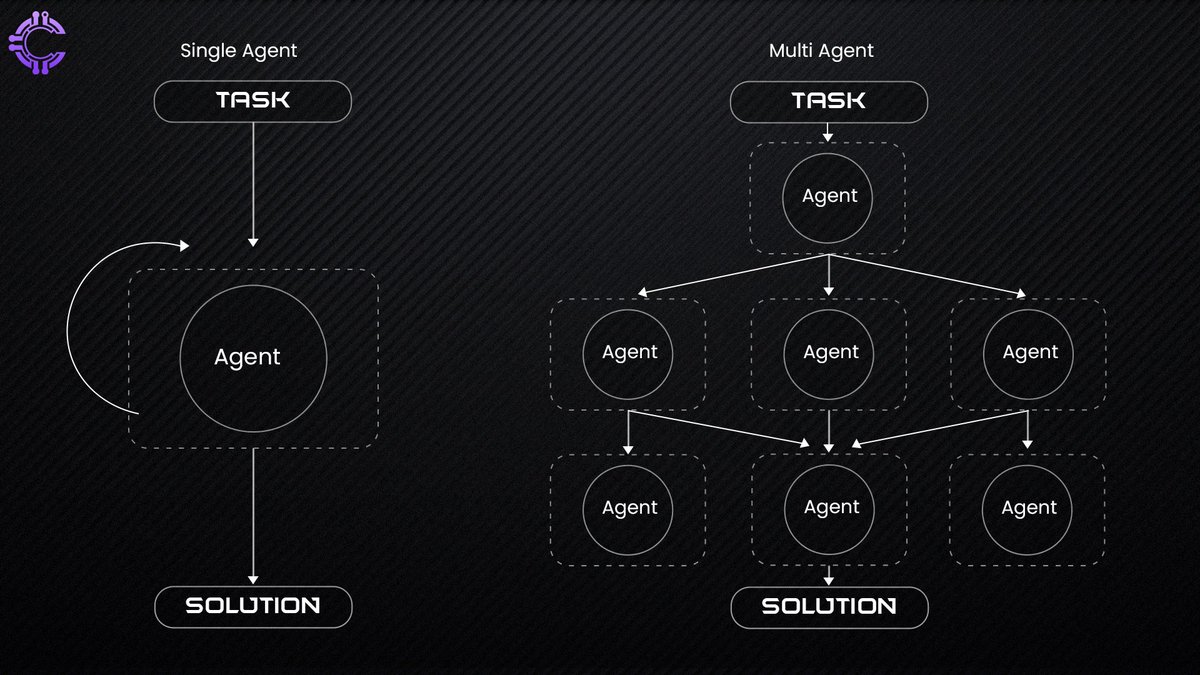
Traditional AI systems operate in a centralized framework, designed to tackle narrow tasks with precision. While effective for specific applications, these systems face challenges in scaling, adapting to new scenarios, and mitigating inherent biases. In contrast, multi-agent systems (MAS) offer a decentralized, collaborative approach that excels in dynamic and complex environments.
MAS operates through a network of autonomous agents that communicate, share knowledge, and coordinate actions without relying on a central authority. This decentralized architecture not only enhances resilience but also enables agents to adapt to new challenges, making the system highly scalable and efficient.
Swarm Intelligence
At the heart of multi-agent systems lies the concept of swarm intelligence, a model inspired by natural phenomena such as ant colonies and bird flocks. These systems showcase how simple agents, working together, can solve complex problems through decentralized decision-making and collective behaviour.

Key Traits of Swarm Intelligence in Multi-Agent Systems
1. Goal Oriented Collaboration:
Agents align their actions toward shared objectives, ensuring that individual efforts contribute to the system’s overall success.
2. Dynamic Knowledge Sharing:
Information flows seamlessly between agents, allowing them to make informed decisions and enhance the system’s collective intelligence.
3. Adaptive Coordination:
Like a flock adjusting its path mid flight, agents continuously adapt to changing conditions and evolving challenges, maintaining efficiency and stability.
This adaptive, goal-driven collaboration makes swarm intelligence a cornerstone of modern decentralized AI systems. By mimicking nature’s best strategies, MAS unlocks new possibilities in fields like logistics, healthcare, and autonomous systems, paving the way for intelligent, self-organizing ecosystems that are not only robust but also transformative.
Real-World Transformations with Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence, inspired by nature’s cooperative systems like ant colonies and bird flocks, is not just a concept, it can drive innovation across industries. With decentralized, goal-driven collaboration, swarm intelligence can enable multi-agent AI to tackle complex, dynamic problems in ways that traditional, isolated systems simply cannot.
Use cases of Swarm Intelligence or multi-agent networks
Swarm intelligence can deliver transformative results in sectors that demand adaptability, precision, and speed:
1. Supply Chain Optimization:
AI-driven swarms can redefine logistics and inventory management. Autonomous agents can continuously monitor demand, track shipments, and optimize routes in real-time. For instance, if unexpected delays occur, agents can dynamically reassign resources to maintain efficiency. This real-time adaptability can significantly reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction.
2. Healthcare Innovations:
Distributed AI agents can revolutionize patient care by collaboratively analyzing vast amounts of medical data. One agent can focus on diagnostic imaging, another can analyze patient history, and yet another can evaluate treatment protocols. Together, they can deliver faster, more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans, potentially improving outcomes and reducing medical errors.
3. Smarter Financial Markets:
Autonomous agents in financial markets can execute trades, manage portfolios, and forecast trends with unparalleled precision. Swarm intelligence can allow these agents to analyze diverse datasets simultaneously, adapt to market shifts, and make decisions in milliseconds, potentially giving traders a competitive edge.
Why Collaboration Outshines Isolation in AI Systems

While traditional AI systems often function as isolated, monolithic entities, multi-agent systems bring diversity, adaptability, and transparency to the table, solving problems more effectively.
Reducing Bias with Diverse Perspectives
Single-agent AI models often inherit biases from their training data, leading to skewed outcomes. Multi-agent systems combat this issue by distributing tasks among specialized agents with diverse perspectives.
Take the example of a legal AI application:
• One agent analyzes case law and precedents,
• Another evaluates client-specific data,
• A third reviews arguments from opposing counsel.
By cross validating their findings, these agents ensure a balanced, fairer decision making process, reducing the risk of bias and improving trustworthiness.
Adapting to Dynamic Environments
Traditional AI struggles to respond to unpredictable changes, but multi-agent systems thrive in such conditions by leveraging their decentralized architecture.
For instance, in autonomous vehicles:
• One agent monitors road conditions and weather,
• Another oversees vehicle diagnostics to detect potential issues,
• A third navigates traffic patterns in real time.
By exchanging data and updating decisions collectively, these agents ensure safety and efficiency, even in rapidly changing environments like rush-hour traffic or unexpected road closures.
Enhancing Transparency and Explainability
As AI systems grow more complex, explainability becomes a critical factor in gaining user trust and meeting regulatory standards. Multi-agent systems address this challenge by decentralizing decision-making, making the process more transparent and easier to understand.
Each agent in the system performs a specific role, and its decisions are traceable. For example, in a decentralized financial advisory platform:
• One agent assesses risk profiles,
• Another evaluates investment opportunities,
• A third monitors real-time market trends.
When these agents collaborate, their individual contributions are recorded on a blockchain or a decentralized ledger, offering a clear, tamper proof audit trail. This approach simplifies compliance with regulations while fostering user confidence.
Challenges of Multi-Agent Systems: Pushing the Boundaries

While multi agent systems (MAS) offer a revolutionary framework for AI, their implementation comes with significant challenges. These hurdles must be addressed to realize their full potential in solving complex, dynamic problems. Let’s explore the core difficulties and how they can be tackled.
1. Communication Overhead: Scaling the Chatter
As the number of agents increases, so does the complexity of communication. Each agent must share and process information in real time, which can lead to bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
For example, in swarm intelligence systems inspired by nature, agents must exchange data rapidly while avoiding redundant or conflicting information.
Without streamlined communication protocols, the system risks becoming inefficient. Techniques like message filtering, priority queuing, and bandwidth optimization algorithms are being developed to manage this overhead. Advanced tools, such as Swarm AI by ChatGPT, showcase how communication bottlenecks can be minimized by enabling real-time collaboration across decentralized agents.
2. Scalability Challenges in Complex Environments
Scaling MAS to operate in large, intricate systems demands substantial computational power and innovative algorithms. A swarm of drones mapping disaster zones, for instance, requires agents to adapt to unpredictable terrain, weather, and communication constraints all while coordinating effectively.
This scalability issue is compounded by the “exponential growth” problem: as agents increase, the complexity of interactions grows exponentially.
Distributed computing frameworks and edge AI solutions where agents process data locally rather than relying on centralized servers are crucial to overcoming this challenge. Additionally, the integration of reinforcement learning allows agents to self-improve as the system expands.
3. Privacy and Security: A Double Edged Sword
Decentralized systems, while robust, are vulnerable to privacy and security risks. In MAS, data flows continuously between agents, making it a tempting target for malicious actors. Risks include:
• Data breaches exposing sensitive information.
• Misinformation campaigns disrupting decision-making.
• Agent manipulation by adversarial attacks.
To address these vulnerabilities, MAS must incorporate end-to-end encryption, blockchain-based verification, and federated learning protocols.
Federated learning ensures agents can train on decentralized data without exposing sensitive information. Furthermore, behavioral anomaly detection algorithms can identify rogue agents attempting to undermine the system.
4. Coordination Complexity: Balancing Autonomy and Collaboration
Ensuring effective collaboration without conflicts is a monumental challenge in MAS. Agents must strike a delicate balance between autonomy and teamwork.
Consider autonomous vehicles: one vehicle might prioritize speed while another prioritizes fuel efficiency. Without robust coordination algorithms, these conflicting goals could lead to traffic gridlock. To resolve this, MAS use distributed constraint optimization and game theoretic approaches, enabling agents to align their strategies dynamically. Advanced frameworks, such as Swarm AI systems, leverage adaptive coordination protocols to ensure seamless collaboration in real time.
Conclusion
Multi agent systems represent a step toward reshaping the future of artificial intelligence. By decentralizing intelligence and fostering collaboration between autonomous agents, these systems offer a more adaptable and efficient way to solve complex, dynamic problems. Rather than relying on a single, centralized entity, multi agent systems enable agents to work together, share knowledge, and make decisions collectively, leading to more robust and scalable solutions.
The journey toward Ultra High Intelligence is both exciting and daunting. Multi-agent systems are more than just a stepping stone, they’re the foundation of a future where intelligence is decentralized, collaborative, and limitless.
However, with great power comes great responsibility. The path to UHI requires us to navigate ethical dilemmas, manage risks, and ensure that these technologies align with human values.
In this new era of AI, collaboration isn’t just a feature it’s the defining characteristic of intelligence. By embracing multi-agent systems, we’re not just advancing technology; we’re reshaping the very concept of what it means to be intelligent.
About Cluster Protocol
Cluster Protocol is the co-ordination layer for AI agents, a carnot engine fueling the AI economy making sure the AI developers are monetized for their AI models and users get an unified seamless experience to build that next AI app/ agent within a virtual disposable environment facilitating the creation of modular, self-evolving AI agents.
Cluster Protocol also supports decentralized datasets and collaborative model training environments, which reduce the barriers to AI development and democratize access to computational resources. We believe in the power of templatization to streamline AI development.
Cluster Protocol offers a wide range of pre-built AI templates, allowing users to quickly create and customize AI solutions for their specific needs. Our intuitive infrastructure empowers users to create AI-powered applications without requiring deep technical expertise.
Cluster Protocol provides the necessary infrastructure for creating intelligent agentic workflows that can autonomously perform actions based on predefined rules and real-time data. Additionally, individuals can leverage our platform to automate their daily tasks, saving time and effort.
🌐 Cluster Protocol’s Official Links:
